The second-order Greeks are a bit extra sophisticated. Fairly than trying on the impression on the choice itself, they measure how a change in one of many similar underlying parameters results in a change within the worth of a first-order Greek.
An necessary second-order metric is gamma. The truth is, it’s the solely second-order Greek that choice merchants use with any regularity. Gamma measures the speed of change of the delta with respect to the underlying asset.
As delta is a primary by-product of the value of an choice, gamma is a second by-product.
To grasp what all this implies, we first have to take a step again and outline what’s the delta of an choice.
Understanding Delta
Choices Gamma Math
It’s not vital to know the maths behind gamma (please be happy to go to the following part if you’d like), however for these gamma is outlined extra formally because the partial by-product of delta with respect to underlying inventory worth.
The method is under (some information of the traditional distribution is required to know it).
Delta refers back to the change of a worth of an choice in regard to the value of the underlying safety. For calls, delta ranges from 0 to 1.
For places, it has a worth of -1 and 0. Delta expresses how a lot the value of an choice has elevated or decreased when the underlying asset strikes by 1 level.
Normally, when choices are on the cash, you may anticipate to see a delta of between 0.5 and -0.5. When choices are far out of the cash, they’ve a delta worth near 0, and when they’re deep within the cash, the delta is near 1.
Which means, usually, name homeowners make a revenue when the underlying inventory will increase in worth, as this results in a optimistic delta. In distinction, as places have a detrimental delta worth, put homeowners see positive aspects when underlying inventory falls.
It’s necessary to notice that this isn’t all the time the case: when one other issue is massive sufficient, it may well offset the info.
Calculating the Impression of Delta
To make use of the above in an instance, think about a name has a delta of 0.5. If the underlying inventory will increase by $1, the value of the decision ought to rise by round $0.50.
If the underlying asset decreases by $1, the value will drop by about $0.50. This assumes, after all, that no different pricing variables change.
Now think about {that a} put has a delta of -0.5. If the underlying inventory will increase by $1, the value of the put will drop by $0.50. If it decreases by $1, although, the value will rise by $0.50.
Possibility holders will discover that the delta of an choice will increase quickly at a sure worth vary — that is referred to as the exploding delta.
For the customer, that is nice information, as it may well result in huge income. After all, the other is true for sellers on the opposite finish of an exploding delta.
The truth is, an exploding delta is a significant motive why promoting unhedged choices incurs such a excessive danger.
Keep in mind, although, that whereas delta hedging can scale back directional danger from actions in worth of the underlying asset, such a technique will scale back the alpha together with the gamma. We’ll now see why that issues.
What Is Gamma?
Gamma specifies how a lot the delta will change when the underlying funding strikes by $1 (a unit of gamma is 1/$).
In different phrases, whereas the delta tells you at what pace the value of the choice will change, the gamma will let you know at what acceleration the change will occur.
Which means you should use gamma to foretell how the delta will transfer if the underlying asset adjustments — and, due to this fact, how the worth of the choice will change.
Gamma is necessary as a result of delta is barely helpful at a specific second in time.
With gamma, you may work out how a lot the delta of an choice ought to change within the case of a rise or lower within the underlying asset.
Why Do We Want Gamma?
To emphasise why gamma issues and the way it provides one other stage of understanding to choices that goes past delta, let’s take an instance. Think about two choices have the identical delta however completely different gamma values.
There’s no have to even use numbers on this instance: it’s sufficient to say that one has a low gamma and the opposite a excessive gamma.
The choice with the excessive gamma will likely be riskier. It’s because if there may be an unfavorable transfer within the underlying asset, the impression will likely be extra pronounced.
In different phrases, if an choice has a excessive gamma worth, there may be an elevated chance of unstable swings. As most merchants favor choices to be predictable, the choice with the low gamma is preferable.
One other solution to clarify that is to say that gamma measures how steady the chance of an choice is.
How Gamma Modifications with the Passage of Time
Because the delta of an choice is dynamic, the gamma should even be always altering. Even minuscule actions within the underlying inventory can result in adjustments within the gamma.
Usually, the gamma reaches its peak worth when the inventory is close to the strike worth. As we already noticed, the utmost delta worth is 1.
Because the delta decreases as the choice strikes additional into or out of the cash, the gamma worth will transfer nearer to 0.
Utilizing Gamma to Measure Change in Delta
Calculating a change within the delta utilizing gamma is sort of simple. For instance, think about ABC inventory is buying and selling at $47. Let’s say the delta is 0.3 and the gamma is 0.2.
Within the case that the underlying inventory will increase in worth by $1 to $48, the delta will transfer as much as 0.5. If, as a substitute, the inventory was to lower in worth by $1 to $46, the delta would drop to 0.1.
Lengthy and Brief Choices with Gamma
For holders of lengthy choices, gamma means an acceleration in income each time the underlying asset strikes $1 of their favor. They’re lengthy gamma.
It’s because the gamma causes the delta of an choice to extend as the choice strikes nearer to the cash or because it turns into additional within the cash.
Due to this fact, each greenback of improve within the underlying asset means a extra environment friendly return on capital.
This similar idea signifies that when an underlying asset strikes $1 in opposition to the holder’s favor, losses decelerate.
On the flip facet, the gamma poses a danger for sellers of choices — since, if there’s a winner within the equation, there additionally needs to be a loser. Simply as gamma accelerates income for holders of lengthy choices, it accelerates losses for sellers.
Equally, because it causes losses to decelerate for the holder, it leads directional positive aspects to decelerate for the vendor.
The Significance of Right Forecasts
Irrespective of in case you’re shopping for or promoting, having an correct forecast is important. As a purchaser, a excessive gamma that you simply forecast incorrectly may imply the choice strikes into the cash and the delta strikes towards 1 sooner than you anticipate.
This may imply the delta will then develop into decrease extra shortly than you predicted.
For those who’re a vendor, an incorrect forecast is simply as problematic. As the choice you offered strikes into the cash, a excessive gamma might imply your place works in opposition to you at an accelerated price. Within the case your forecast is correct, nonetheless, a excessive gamma may imply the offered choice loses cash sooner, yielding optimistic outcomes for you.
How Volatility Impacts Gamma
The gamma of choices on the cash is excessive when volatility is low. It’s because low volatility happens when the time worth of an choice is low. Then, you’ll see a dramatic rise when the underlying inventory nears the strike worth.
When volatility is excessive, nonetheless, the gamma is often steady throughout strike costs. The rationale for that is that when choices are deeply within the cash or out of the time, the time worth tends to be substantial.
As choices strategy the cash, there’s a much less dramatic time worth. In flip, this leads the gamma to be each low and steady.
Expiration Danger
Another side to think about is the expiration danger. The nearer an choice is to expiration, the extra slim the chance curve.
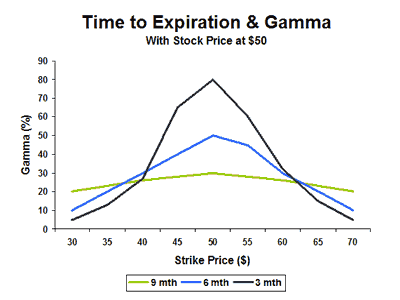
The shortage of time for the underlying property to maneuver to far out-of-the-money strikes reduces the chance of them being within the cash. The result’s a extra slim delta distribution and a extra aggressive gamma.
The most secure approach to make use of understanding of gamma to your benefit is to roll and shut your positions a minimum of seven (or maybe as many as 10) days earlier than expiration.
For those who wait longer than seven days out, there’s a larger probability you’ll see drastic swings — the place dropping trades convert into winners and vice versa. Patrons might be able to profit from this development, however it’s notably dangerous for sellers.
Record of gamma optimistic methods
Record of Gamma detrimental methods
- Brief Name
- Brief Put
- Brief Straddle
- Brief Strangle
- Vertical Credit score Unfold
- Lined Name Write
- Lined Put Write
- Iron Condor
- Butterfly
- Lengthy Calendar Unfold
Abstract
- Gamma measures the speed of change for delta with respect to the underlying asset’s worth.
- All lengthy choices have optimistic gamma and all quick choices have detrimental gamma.
- The gamma of a place tells us how a lot a $1.00 transfer within the underlying will change an choice’s delta.
-
We by no means maintain our trades until expiration to keep away from elevated gamma danger.
In regards to the Creator: Chris Younger has a arithmetic diploma and 18 years finance expertise. Chris is British by background however has labored within the US and these days in Australia. His curiosity in choices was first aroused by the ‘Trading Options’ part of the Monetary Occasions (of London). He determined to deliver this information to a wider viewers and based Epsilon Choices in 2012.
Associated articles


